How to Reinstall the Veeam Transport Service on a Linux Server
The steps outlined in this article are used as a troubleshooting step when an issue occurs with a Linux server that requires that the Veeam Transport service be manually reinstalled.
When phasing out a Linux server, these steps are not necessary; In such a scenario, simply removing the Linux server from Veeam Backup & Replication will cause the Veeam Transport Service to be uninstalled from the Linux server.
Purpose
Solution
The uninstall procedure will cause all Veeam Backup & Replication tasks currently utilizing the Linux server to fail. As such, it is highly recommended to ensure that either no tasks are occurring within Veeam Backup & Replication or that the Linux server is not currently being used by Veeam Backup & Replication.
Generally speaking, if the Linux server is being used by a Veeam Backup & Replication task, there will be a 'veeamagent' process active. Use the following command to check for active 'veeamagent' processes:
ps -e | grep veeamagent
Uninstall Veeam Transport Service
The following commands are to be executed on the Linux server.
Expand the section that aligns with the version of Veeam Backup & Replication that deployed the transport service on the Linux server.
Starting with Veeam Backup & Replication (VBR) v12.1.2, the VDDK libraries are deployed as a separate package from veeamtransport. This change ensures that the VDDK libraries are only installed on managed servers that need to interact directly with VMware ESXi.
On Linux-based VMware Backup Proxies, if the veeamtransport package is removed, the VDDK libraries (vmware-vddk) will be removed as well due to their dependency on the veeamtransport package.
You can force VBR to check for and deploy the vmware-vddk package by editing the proxy entry under Backup Proxies in the Backup Infrastructure view and then proceed through the wizard steps.
Redeploy Veeam Transport Service to Linux Server
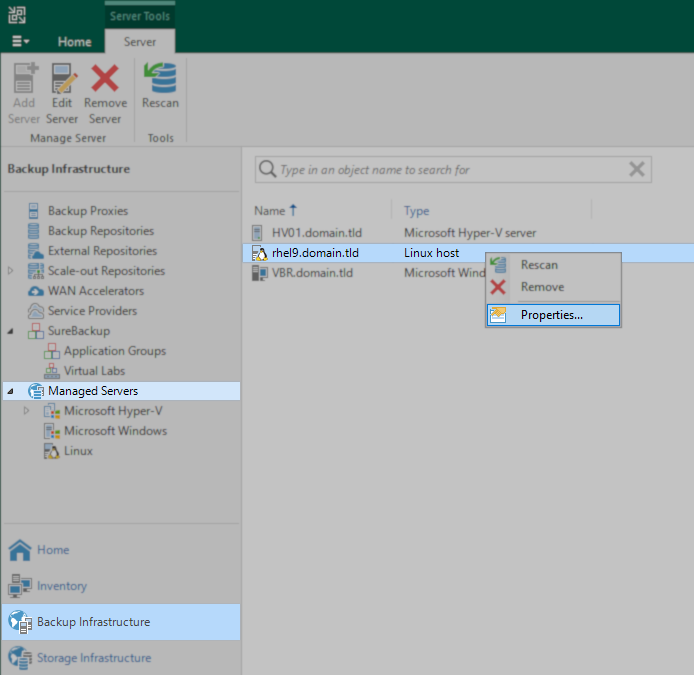
- Open the Veeam Backup & Replication Console.
- Within the view selector in the bottom-left corner, select Backup Infrastructure.
- Within the tree in the Backup Infrastructure navigation pane, select Managed Servers.
- Within the working area, identify and edit the entry for the Linux server.
- In the Edit Linux Server wizard, click the Finish button.
Veeam Backup & Replication will notice that the Veeam Transport service is missing and redeploy the Veeam Data Mover.
More Information
To report a typo on this page, highlight the typo with your mouse and press CTRL + Enter.
Spelling error in text
KB Feedback/Suggestion
This form is only for KB Feedback/Suggestions, if you need help with the software open a support case