- Veeam Support Knowledge Base
- Restoring Domain Controller from an Application-Aware backup
Restoring Domain Controller from an Application-Aware backup
Cheers for trusting us with the spot in your mailbox!
Now you’re less likely to miss what’s been brewing in our knowledge base with this weekly digest
Oops! Something went wrong.
Please, try again later.
The details discussed in this article are related only to Domain Controllers that are not virtual machines in a Hyper-V environment.
In Hyper-V environments, Domain Controller VMs are not modified to change the boot method during restore because the HV Integration Tools notify existing Domain Controllers of the restored DC's state.
Challenge
This article documents Domain Controller restore scenarios and steps to perform proper DC recovery. Depending on the scenario, additional steps may be required to complete a DC restore.
Note regarding restore of DC if VM was backed up with Veeam Backup & Replication:
All scenarios below assume that if the DC was a VM and backed up using Veeam Backup & Replication, application-aware processing was enabled during backup. When application-aware processing is enabled for a DC VM, backed up by Veeam Backup & Replication, the post-restore boot procedure is modified so that the DC will restore into a non-authoritative state.
For restores of Domain Controller backed up using Veeam Agent for Microsoft Windows:
Veeam Agent for Microsoft Windows modifies the post-restore boot procedure regardless of application-aware setting. Meaning that the restore of a DC backed up using Veeam Agent for Microsoft Windows will always result in restored DC booting into a non-authoritative state.
Solution
Non-Authoritative Restore (Default)
Restore a single DC to an environment where there are other functioning DCs (or when it was the only DC)
This scenario assumes:
- The Domain Controller is being restored to an environment where other Domain Controllers are present from which the restored Domain Controller can replicate information.
or - The Domain Controller being restored is the only Domain Controller that exists in the environment.
In this scenario, a simple non-authoritative restore is sufficient to recover.
Restore the Domain Controller. The steps taken by Application-Aware Processing during the backup process will cause the Domain Controller to be restored in a non-authoritative state. The restored Domain Controller will first boot into Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) mode, then automatically reboot into a normal state. The Domain Controller will know that it has been recovered from backup and will allow the other DC's in the environment to update it.
When restoring a Domain Controller as the single Domain Controller in an environment, the same boot cycle will occur after restore (DSRM boot, automatic-reboot, normal boot). After the automatic reboot, the restored DC will enter an operational state.
Authoritative Restores
The scenarios below require knowing whether the Domain Controllers used DFS-R or FRS to handle the SYSVOL replication.
If you are unsure which replication technology was in use, review this Microsoft article section:
Determining Whether a Domain Controller's SYSVOL Folder is Replicated by DFSR or FRS
Generally speaking, FRS was used with Server 2003 or Server 2008 Domain Controllers.
If the domain functional level is Windows 2008 or above, you can use the following command to check if the Domain Controller is in the ‘ELIMINATED’ state which indicates DFSR is in use:
dfsrmig.exe /getglobalstateRestore the entire AD infrastructure (AKA “all DC’s are lost”) where DFSR SYSVOL Replication was used
After restoring a Domain Controller, the automatic recovery process performs a non-authoritative restore, causing the Domain Controller to begin seeking replication partners. However, in a scenario where all Domain Controllers are lost, and there are no partners available, replication may take quite a long time to start (e.g., 15-30 minutes). To avoid wasting time attempting to contact replication partners, it is recommended to restore two domain controllers at once. Power them on and wait for their reboot. Then, force one of them to become authoritative for SYSVOL (see below) so that they can start replicating. After that, restoring additional Domain Controllers will not require post-restore steps.
Note: During the restore procedure, make sure the restored DC’s DNS records point to available DNS servers (e.g., to itself).
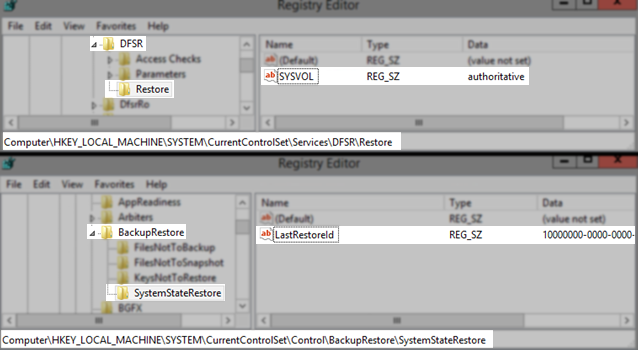
For Domain Controllers using the DFS-R to replicate SYSVOL, you must perform an authoritative restore of the SYSVOL on the first DC restored, by setting the following registry values as shown here:
- After the Domain Controller reboots, navigate to HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\DFSR registry hive, create a key named Restore and within that key create REG_SZ (string) named SYSVOL and set the value to authoritative.
- Then, navigate to HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\BackupRestore, create a key named SystemStateRestore and within that key create a REG_SZ (string) named LastRestoreId with any GUID value. (Example: 10000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000).
- Restart the DFSR service.
REG ADD "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\DFSR\Restore" /v SYSVOL /t REG_SZ /d authoritative /f
REG ADD "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\BackupRestore\SystemStateRestore " /v LastRestoreId /t REG_SZ /d 10000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 /f
NET STOP DFSR
NET START DFSRNote: If you’re restoring a DC without FSMO roles, you may want to transfer them to it manually after the restore, using the ntdsutil seize command.
If the first DC that was restored is already hosting operations master roles, set the following registry value in order to bypass initial synchronization requirements and not to wait for another partner to replicate the directory partitions:
Key Location: HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NTDS\Parameters
Value Name: Repl Perform Initial Synchronizations
Value Type: DWORD (32-Bit) Value
Value Data: 0
After setting the value above, restart the domain controller.
Note: Don’t forget to reset this value back to 1 after domain recovery is completed, so that the domain controller requires successful replication with its partners before starting to service client requests.
Restore the entire AD infrastructure (AKA “all DC’s are lost”) where FRS SYSVOL Replication was used
After restoring a Domain Controller, the automatic recovery process performs a non-authoritative restore, causing the Domain Controller to begin seeking replication partners. However, in a scenario where all Domain Controllers are lost, and there are no partners available, replication may take quite a long time to start (e.g., 15-30 minutes). To avoid wasting time attempting to contact replication partners, it is recommended to restore two domain controllers at once. Power them on and wait for their reboot. Then, force one of them to become authoritative for SYSVOL (see below) so that they can start replicating. After that, restoring additional Domain Controllers will not require post-restore steps.
Note: During the restore procedure, make sure the restored DC’s DNS records point to available DNS servers (e.g., to itself).
For Domain Controllers using the FRS to replicate SYSVOL, you must perform an authoritative restore of the SYSVOL on the first Domain Controller restored using burflags, as shown here:
- Open Registry Editor
- Navigate to HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NtFrs\Parameters\Backup/Restore\Process at Startup
- Double-click on BurFlags
- Assign it a value of D4 (hex) or 212 (dec)
- Open the Services Panel
- Stop the NTFRS Service
- Start the NTFRS Service
Alternatively, you can use the following commands in an Administrative Command Prompt:
REG ADD "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\NtFrs\Parameters\Backup/Restore\Process at Startup" /v BurFlags /t REG_DWORD /d 212 /f
NET STOP NTFRS
NET START NTFRS You can then monitor the status of the replication by searching for the Event ID 13516 in Event Viewer (eventvwr.msc)

Restoring due to Active Directory corruption
A scenario where no Domain Controllers are actually lost, but Active Directory itself is damaged somehow (e.g., corrupt objects or schema), and you need to restore from a backup created before the corruption occurred. In this case, you need to restore one of the Domain Controllers while the others still operate in a damaged state and then force them to accept replication changes from the restored Domain Controller. To do so will require an authoritative restore of the Domain Controller.
Note: It is recommended to restore the Domain Controller with the network disconnected to prevent it from accepting changes from the other Domain Controllers after the default non-authoritative restore.
Note: For an easier item-level recovery of Active Directory objects (without the need to restore the Domain Controller itself), consider using Veeam Explorer for Active Directory.
To perform an authoritative restore:
- Restore the Domain Controller and let it complete the default non-authoritative restore (i.e., wait until it boots a second time).
- During this second boot, press F8 to get to DSRM mode.
- Log in with the DSRM account and password.
- Open a command prompt and run ntdsutil command.
- Per Microsoft Documention:
Before you can run the authoritative restore subcommand, you need to set NTDS or an AD LDS instance as the active instance for Ntdsutil. For example, if the AD LDS instance that you want to restore is named instance 1, type the following command at the ntdsutil: prompt before you run the authoritative restore subcommand, and then press ENTER:
activate instance instance 1 - Then, type "authoritative restore" and press Enter.
- Mark objects as authoritative:
- To mark a single object as authoritative, type
restore object <distinguished_name>
where <distinguished_name> is the DN of the object. - To mark a subtree of objects as authoritative, type
restore subtree <distinguished_name>,
where <distinguished_name> is the DN of the subtree.
This will mark the container object and everything it contains as authoritative.
Note: If the DN contains one or more spaces, enclose the entire DN in quotes.
- To mark a single object as authoritative, type
- At the Authoritative Restore Confirmation dialog box, click Yes.
- Upon restore completion, type "quit" and press Enter to exit the ntdsutil utility.
- Reboot server.
- Perform an authoritative restore of the SYSVOL; as documented in the scenarios above, the next steps will depend on the SYSVOL replication technology in use (DFS-R or FRS). After the Domain Controller is forced into an authoritative state, reconnect the network.
More Information
Restoring very old restore points for a Domain Controller can have some side effects due to Kerberos certificate updates and related trusts (check event logs of the restored server). See also: KB2226.
In situations where data from very old restore points are needed, it is advisable to use Veeam Explorer for Active Directory for granular item-level AD restore methods. Check out the "compare" feature in the Active Directory Explorer.
To report a typo on this page, highlight the typo with your mouse and press CTRL + Enter.
Spelling error in text
Thank you!
Your feedback has been received and will be reviewed.
Oops! Something went wrong.
Please, try again later.
You have selected too large block!
Please try select less.
KB Feedback/Suggestion
This form is only for KB Feedback/Suggestions, if you need help with the software open a support case
Thank you!
Your feedback has been received and will be reviewed.
Oops! Something went wrong.
Please, try again later.